Welcome to the dental practice
Thomas Hamann
and Partners
Berlin Wittenbergplatz
Our services
Successful treatments require a strong team with competent service. Therefore, individual and personal care is particularly important to us during the entire treatment. First-class dentistry awaits you with us in the heart of Berlin with the latest digital diagnostics and our own dental laboratory. We also specialize in laser dentistry and have an integrated training center. In order to make your dentist stay as pleasant and pain-free as possible, good care is a matter of course, so that we provide you with a healthy and radiant smile. In our barrier-free and modern practice, we offer intensive support and advice. You can rely on our many years of experience in the fields of implantology, laser dentistry and temporomandibular joint diagnostics. We treat you with the latest technology in a pleasant and relaxed atmosphere.
Implantology:
Implantations
More quality to life due to tooth implantations
If a gap in the teeth is to be closed or a whole row of teeth is to be replaced, the treatment within regular dental medicine is limited. Implants can be used when the absence of suitable critical points, e.g. the natural teeth necessary for the procedure no longer exist. The implants allow functional, high-quality and aesthetic tooth replacements.
Today, dental medicine can offer solutions which were inconceivable in the past. Gaps, or even completely toothless patients are treated in no time.
Nowadays many people live with artificial roots. In virtually hopeless cases functional, high-quality dentures are possible using implants. However, implant care also has its limitations. The cooperation of the patient is essential to guarantee a long-term survival of the implant. Only patients who pay attention to their oral hygiene can be helped with implants.
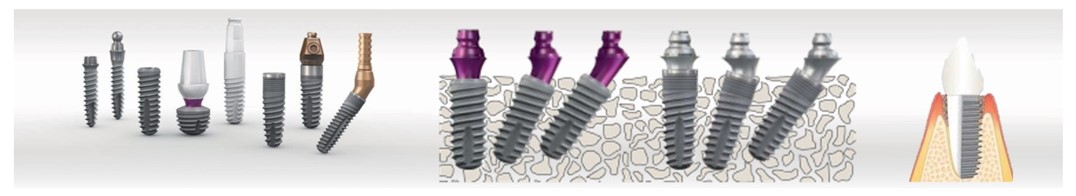
Ex.: Screw implants
What are implants?
An implant (lat.) is an artificial body which is „planted“ into a living organism.
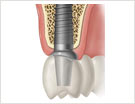
Implants replace missing teeth, including the root. They substitute the former teeth in the jawbone. During recovery, the bone fuses with the implant, enabling it to sit solidly. For at least three months, the implant lies below the oral mucosa, which acts as a protectorate. Afterward an additional device is screwed into the implant, onto which the „new tooth“ is then firmly anchored like a customary dental crown.
Instead of the root, the implant receives the pressure caused by chewing and initiates it into the jaw.
Who is in need of implants?
The purpose of every prosthetic dental treatment was always to replace the loss of the natural tooth as realistically as possible. However, the less teeth there are, the more difficult it becomes to reach this goal. Often a flawless function with extensive duration is not possible using prosthesis, due to the changes of the jawbone and the oral mucosa. Over time the prosthesis ceases to fit exactly and looses it’s hold.
In many of these cases, dental implants allow for a more optimal solution. Implants are possible for all toothless patients with bad dentures and for patients with big and small tooth gaps.

Ex.: Screw implants
Photos: approved by Sybron Implant Solutions GmbH
Which material do implants consist of?
The material that implants consist of has to be acceptable to the body. Dental implants are comprised primarily of titanium which also acts as a bone like coat. The application of material and the type of implant which is to be used depends on each individual patient. Thus the implant cannot result in a material-conditioned rejection.
How are implants applied?
Previous to the treatment with implants, every patient is thoroughly examined. Periodontosis and cavities in affected teeth must be treated beforehand. In case of a present general illness a consensus with the family doctor might be necessary. If the diagnosis calls for an implantation, the treatment follows a detailed discussion and clarification with the patient. The planning can begin and the operation smoothly carried out. The intervention is carried out under local anesthesia. According the the number of implants being used, the operation lasts between 30 and 90 minutes.
After the implant bed is prepared, the implant is inserted and the mucous membrane sewn closed again. The mucous membrane protects it against unfavorable strain during the recovery phase. Depending on the individual situation, the implant heals into the jawbone after 3 to 6 months. The patient receives an intermediate solution and attends regular check-ups during this time.


Ex.: Screw implants
Photos: approved by the company Straumann
How long do implants last?
The patient himself is responsible for the long-term success of the implant. An accurate and careful oral hygiene ensure protection against dental plaque and infections which could endanger the implants.
Many patients carry their implants free of pain indefinitely. If the patient adheres to all advice given, he will have a lot of satisfaction with his „third teeth“ for a long time.
Who pays for the implants?
Treatment involving implants is partially covered by most state health insurance plans, however this varies according to individual plans and the patients needs.
Private health insurance plans usually cover a large portion or up to 100% of the of the fees.
A better quality to life with implants
The „new teeth“ provide the patient with renewed self-esteem and a better quality of life. The set of dentures are barely noticeable to the wearer or to others. The functional and aesthetic benefits of implants can achieved at an affordable price. Commonly called „thirds“ can be used as natural teeth.
Implant prosthesis:
After the implantation, the artificial roots must merge with the natural bone. This usually happens easily and without repulsive reactions. Hazards for this important process are primarily bacterial infections between the implant and gums which can lead to so-called Periimplantitus and endanger the hold of the implant. Common causes of these infections are pre-existing illnesses of other teeth, for instance, Parodontitis, or the bacterial plaques which result from insufficient oral hygiene.
Only if the implants have grown together stiffly with the bone apparatus and are diagnosed without infections after rehabilitation, the implantation can be considered successful and the real prosthetic care begins. Here there are many types of substitutes and materials that the gap needing to be filled depends on. Whether single crown or bridge, the variants are diverse and must be customized from case to case, depending on the patient’s situation. For implant patients there is no age limit, because implants are basically usable without risk. However, implants require good care. Hence, a thorough oral hygiene and participation in the semi-annual prophylaxis check-up in the dentist’s practice are essential.
Surgery
Laser in the dental surgery
For more than forty years lasers have been applied in medicine and dental medicine. Primarily in therapy as well as in diagnostics. Our practice also uses the laser in surgery, and this for good reasons:
- The oral mucosa is a very good blood supplied organ. With the application of a laser in surgical interventions in this area, an operation occurs almost completely without bleeding and considerably less traumatically.
- the treatment occurs less painfully and an anesthesia is hardly necessary. After the numbing effect the patient is usually already pain free.
- surgical cuts are much more precise than with a scalpel and there is virtually no loss of healthy tissue.
- No seam is required and
- Extracted tissue can be used for histological examinations
- In addition, healthy tissue is obtained by exact selection and is not damaged.
- In contrast to the application of an electric scalpel during the removal of tissue, patients can also be treated with a cardiac pacemaker.
Possible operational areas for a laser in dental surgery are
- the opening of abscesses
- the gingivectomy (gum demolition during the formation of pockets)
- the removal of the tooth’s root points (WSR) or the exposure of teeth.
- as well as herpes- & aphtha treatment
We perform all dental surgical interventions in our practice.
In addition there is/are:
- Extractions;
- Removal of Wisdom teeth;
- Root tip resections;
- Cyst operations;
- Lips and tongue plastic bands by means of a laser;
- Abscess openings by means of a laser;
- Practice excisions and fine tissue examination;
- Jaw reconstruction (Augmentation);
- Implantology
The majority of surgical procedures can also be done without the use of a laser when requested.
 |
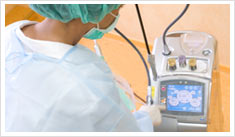 |
|---|---|
| Preparation of the OP | Application of the WaterlaseMD™ |
Aesthetic dentistry:
Aesthetics
Aesthetic aspects of modern dentistry have won themselves an important place in recent years. Previously, the main focus of dental activity lay in the reconstruction of defects. Today, this and the striving to a perfect appearance dominate. Suitable fillings made from plastic and ceramics as well as ceramic crowns and veneers are the various applications used in dental coloring.
What are veneers?
Veneers are thin, nearly transparent ceramic bowls. The tooth in need of a veneer is sanded 0.7 mm on the exterior surface and approx. 1 mm on the edges. In special cases there are exceptional ceramics which do not require a sanding of the tooth if correctly indicated. These ceramics distinguish themselves by a layer thickness of approx. 0.3 mm.
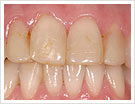 |
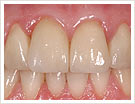 |
| Image 1 | Image 2 |
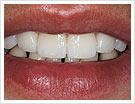 |
 |
| Image 3 | Image 4 |
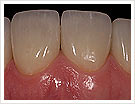
Image 1: source situation
Image 2: final situation
Image 3: veneer blend from the front
Image 4: dental row with veneer blend
Photos: approved by Olaf v. Iperen
Where can veneers be used concerning aesthetic improvement?
- unsightly tooth structures or darkened tooth color
- front teeth with many fillings of different coloring
- damage of the front teeth as a result of accidents
- small dispositions of the front teeth without additional jaw-orthopedic therapy
Advantages of veneers
The largest part of the tooth substance is spared, because the veneers are individually formed by the dental technician and stuck on the prepared tooth surfaces with special adhesives. Veneers show no edges in the gums, the crossing to the natural tooth is invisible. This way a flawless aesthetic result is achieved. The functional efficiency of a tooth with veneer resembles that of a healthy tooth – it is completely resilient.
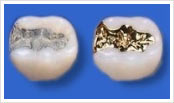
Amalgam replacement
Amalgam in everyone’s mouths
This equivocal sentence describes the problem confronting dental medicine during the past years. As a result of public discussions, patients are aware and unnerved about the risks concerning the application of amalgam as a dental-medical filling material.
Since amalgam was traditionally used exclusively and without limitation as a filling material, the majority of the population feels directly affected. More and more amalgam fillings are now being exchanged with other filling materials.
This is partially due to cosmetic reasons, as amalgam is a very dark material and so impairs a “beaming white smile”. In addition amalgam is composed out of different metals, which makes patients question whether or not it might jeopardize their health. Furthermore, dentists recommend the exchange of amalgam for clearly defined reasons – for example over sized, under sized or broken fillings. Other possibilities are to use different kind of synthetic fillings and inlays made of ceramics or gold.
Reasons for the exchange of amalgam fillings – patient’s wishes
Patients themselves sometimes prefer the exchange of the amalgam fillings for cosmetic reasons, meaning they prefer not to have dark fillings as they value an all round “white” smile or because they favor a high quality therapy.
Some patients also express health-related worries concerning the exchange: They fear that different metal fillings may lead to micro streams, with the result of health damages. Other patients fear that amalgam is the reason for their health discomfort.
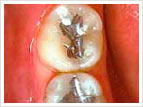
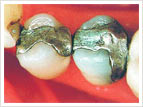
Amalgam fillings
Reasons for the exchange of amalgam fillings – dental-medical recommendation
An amalgam exchange can occur, in certain cases, on the recommendation of the dentist. The reasons can be over sized, under sized or broken fillings, fillings without contact to the recumbent or opposite tooth, those with cavaties on the edge or ones which have been „repaired“several times, fillings which are visible when the patient smiles or with patients who suffer from mercurial idiosyncrasy (extremely sensitive to mercury).
The exchange of amalgam is performed under individually necessary precautions and ranges from strong water application with good suction up to putting on a so-called suitcase dam (elastic rubber protection). A variety of synthetic fillings and ceramic or gold inlays are possible substitutes.
In some cases an amalgam removal is also possible in a medicinal way.
What is this material really all about?
Amalgam is a substance consisting a metal powder and mercury (HG). If a silver-tin-copper-powder is mixed with mercury, a knead-able malleable paste arises: the dental-medical amalgam. Extensive and intensive mixing of the components is decisive for the qualities of the amalgam. Approximately 10 – 30 minutes remain afterward for the dentist to apply the filling material in the tooth and to mold the suitable form for the desired bite. After one hour, the filling is able to withhold a certain load – after 24 hours it has reached the expected firmness.
The advantages of the material are based on the following points
- all in all an easy, inexpensive and quick filling technology is possible,
- it is usable in a variety of ways and easy to process
- no high demand appears in relation to a form of the dental defect
- high breaking and pressure resistance
- long durability and clinically tested
However, the disadvantages are
- aesthetically unattractive color
- not usable in the front teeth area
- fractures give way to possibility of renewed caries formation
- discolorations of the tooth
- indispensability of an under filling
- health danger for the dentist if not processed correctly
- potential allergic and toxic danger by – even if low – an additional burden of the organism by mercury.
From copper amalgam, very seldom from noble amalgam, mercury (Hg) can penetrate the organism in the smallest amounts. Indeed, it can be spoken of an Hg endangerment, yet not of an Hg poisoning.
- copper amalgam should cease to be used
- the correct processing of the amalgam is important in order keep the Hg delivery as low as possible; noble amalgam seldom dissolves
Application restrictions
- retrograde root fillings, since the material comes in direct contact with the bone tissue
- construction fillings under poured crowns, as the meeting of two different metals causes electric conductivity
Tooth-colored fillings
Not only dark amalgam fillings impair a flawless smile in the otherwise white set of teeth and prevent a satisfying aesthetic appearance. White fillings can also seem dark every now and then, since they do not become brighter while bleaching the teeth but keep their color. The whiter the natural teeth become after the filling, the more urgent an exchange or a treatment of the fillings becomes. Different procedures and materials help the situation:
Composites
Synthetic fillings with the so-called composites are used in the front teeth area with damage in the neck of a tooth, or for small to medium-sized fillings in the side teeth area. They are substance-friendly, aesthetically attractive and reasonably priced. They can be processed in a single treatment and are, in small to medium-sized fillings, just as with larger fillings almost as long-lasting as the well know yet aesthetically less attractive amalgam. In the front teeth area, composite is also suitable for the restoration of the original dental form, for example, for accident-related broken tooth edges. These are supplied with special composites and by the layering of several tones a natural appearance is accomplished. An especially intensive oral hygiene is exceedingly important with synthetic fillings, because light discolorations can develop on the edges of the filling. There is not a higher risk of cavities originating in this area than with other filling materials if the teeth are cleaned thoroughly.
However, in comparison to other filling-materials (generally to ceramic inlays) composite has deficits.
For example, with regard to the wearing of the material in contrast to ceramics and gold, as well as concerning the color stability in contrast to ceramics, and the form stability in contrast to ceramics and gold.
In addition, the costs for synthetic fillings in the side teeth area are taken care of by the health insurance only as far as amalgam fillings would have been covered. If the fillings are to be done for purely aesthetic reasons, health insurance plans do not cover the cost of the procedure.
Ceramic inlays
Concerning larger defects in the side teeth area, ceramic inlays are the most considerable and longest-lasting option. In contrast to direct fillings, ceramics cannot be worked on in the mouth. Hence, an impression of the teeth is taken and sent to a dental lab where dental technicians make the „inserts“ precisely and adapt them to the natural color of the teeth. At the next appointment, the inlays are inserted into the tooth with the help of tooth-colored composites. Optically the result is so perfect that the tooth seems completely untouched. Due to the flawless chewing stability and virtually non abrasive material, ceramic inlays are a long-lasting, though 3 to 4 times more expensive solution to composite fillings.
A quickened inlay integration allows the so-called Cerec procedure. The prepped tooth or the impression model is photographed with a special camera. Using the data obtained from the special photographic technology, a computer constructs the inlay and mills it out of a ceramic block.
For bleached teeth ceramic masses, as well as Cerec-ceramic blocks, are available in special colors.
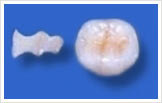 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|
| ceramic inlay | plastic / gold filling | ceramic frame |
Prosthetics:
Jawbone diagnostics
Manual and instrumental FAL and Cadiax
The jaw joint is the most complex joint in our body. Not only because it is a so-called „turn-and-slide joint“, but also because when the right jawbone moves, so does the left one. In addition, the left jawbone moves to the middle while the right one may either not move at all, or in random directions.
All movements, in particular the non-physiological ones, may now cause pain – either by pressure on the so-called bilaminar zone, located behind the jaw heads or by irritation caused by a shifted discus (so-called „shock absorber“ between jawbone heads and jaw sockets). However, pain may also be released by disruptions of different jaw structures.
To find the cause of the patients pains, precise diagnostics with accompanying examinations and individual questioning must be carried out.
During the following functional analysis, a detailed examination of the chewing system is carried out. Considering the results of this examination, suitable procedures to release or remove pain are arranged. According to the diagnosis, other approaches may be necessary to locate the source of the ache. The concluding therapy (e.g. biting rails, coping with stress caused by crunching and pressing, medicinal therapy and physiotherapy) is adjusted according to the needs of the patient.
Pains in the area of the jawbone and the chewing musculature, joint noises (rubbing and/or cracking), restriction of mandible mobility and tensing of the chewing musculature often originate in the teeth. Crooked teeth, tooth loss, defective set of dentures, poor fillings as well as the crunching and pressing of the teeth (stress) can be the cause of discomfort in the jawbone area. Due to the close proximity of jaw and ears, jaw pains are often mistaken as an ear ache. In such cases the ear, nose and throat specialist often finds no explanation for the pains. Jawbone, chewing musculature and teeth form a unity, which means that diagnostics and especially the therapy must take all components of this united system into consideration. Principally the jawbone should not be thought of in isolation, but as a part of the whole. This means that, for example, a dislocated spine or a tense back musculature may originate in the region of the jawbone and vice versa.
Causes of pain in the area of the jawbone:
- Joint-related causes, for example misalignment of the joint disc (cracking while opening of mouth, mouth opening restriction and grater noises)
- Arthritis (ruptured joint disc – bone rubs on bone)
- Muscle pains – tensing of the chewing musculature by crunching or rubbing of the teeth (released by stress, missing teeth and poor set of dentures)
Functional analysis
A precise diagnostic with detailed questioning and examining of the patient is always necessary to find the cause of pains.
First a functional analysis is carried out. This includes a detailed examination of the chewing system. On account of the knowledge gained following the examination procedures, further courses of action, for example visual procedures (X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging), measurements etc., must be taken.
According to the diagnosis, different therapies can be indicated, e.g. bitting rails, coping with stress (crunching, pressing), medicinal therapy and physiotherapy. This reaches from light grinding of the interrupting contacts in the available teeth up to a newly formed set of dentures.
 |
 |
|---|
Manual and instrumental analysis
Concerning the diagnostics, a functional and instrumental analysis must always be carried out before the previously mentioned visual procedures.
The difference between manual and instrumental functional analysis is the they basically pursue different purposes. Manual functional analysis covers the structures of the jawbone which have fallen ill. So-called “pressure technologies” determine the damaged structures by putting adequate pressure on the jawbone. With suitable experience and technology the finest damaged areas can be identified.
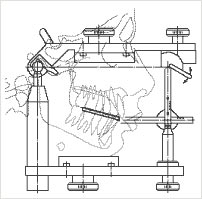
Instrumental functional analysis, primarily depends on the individual movement of the jaw, as there can be considerable differences. Either the motion path is monitored on paper records two-dimensionally, using old technologies, or is analyzed by means of electronic writing utensils and computer support three-dimensionally. This way the articulator (also called chewing simulator) is essentially programmed to analyze the motion paths and determine the damaged places more precisely. Particularly here the Cadiax, IPR and DIR system should be applied.
 |
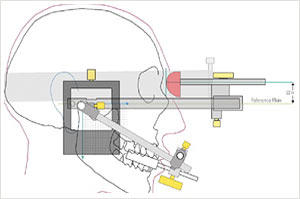 |
|---|---|
| Pattern of a chewing simulator (articulator) | The attached Cadiax-facial curve in the pattern |
Prostetics
If teeth are strongly damaged or lacking a root, it is necessary to strengthen them, otherwise they become fragile and porous. If teeth are missing or must be removed, a prosthesis can substitute them with its varied functions. There are different methods of applying, bridges or prosthesis.
The dental-medical prosthetic designates the medical field that deals with the treatment, care and ministering of tooth loss or distinctive damage to the hard tooth substance. All aspects of the treatment are summarized into this statement: biological, functional, psychosocial, materialistic and technological. As an expert in dental medicine and prosthetic, the dentist has a high degree of responsibility toward the patient.
In the foreground of our treatment there is always a patient-oriented, preventive, health-based initiative, in order to ensure an optimal solution to every individual patient. Special, very modern devices and technologies are available in our practice.
Crowns and bridges
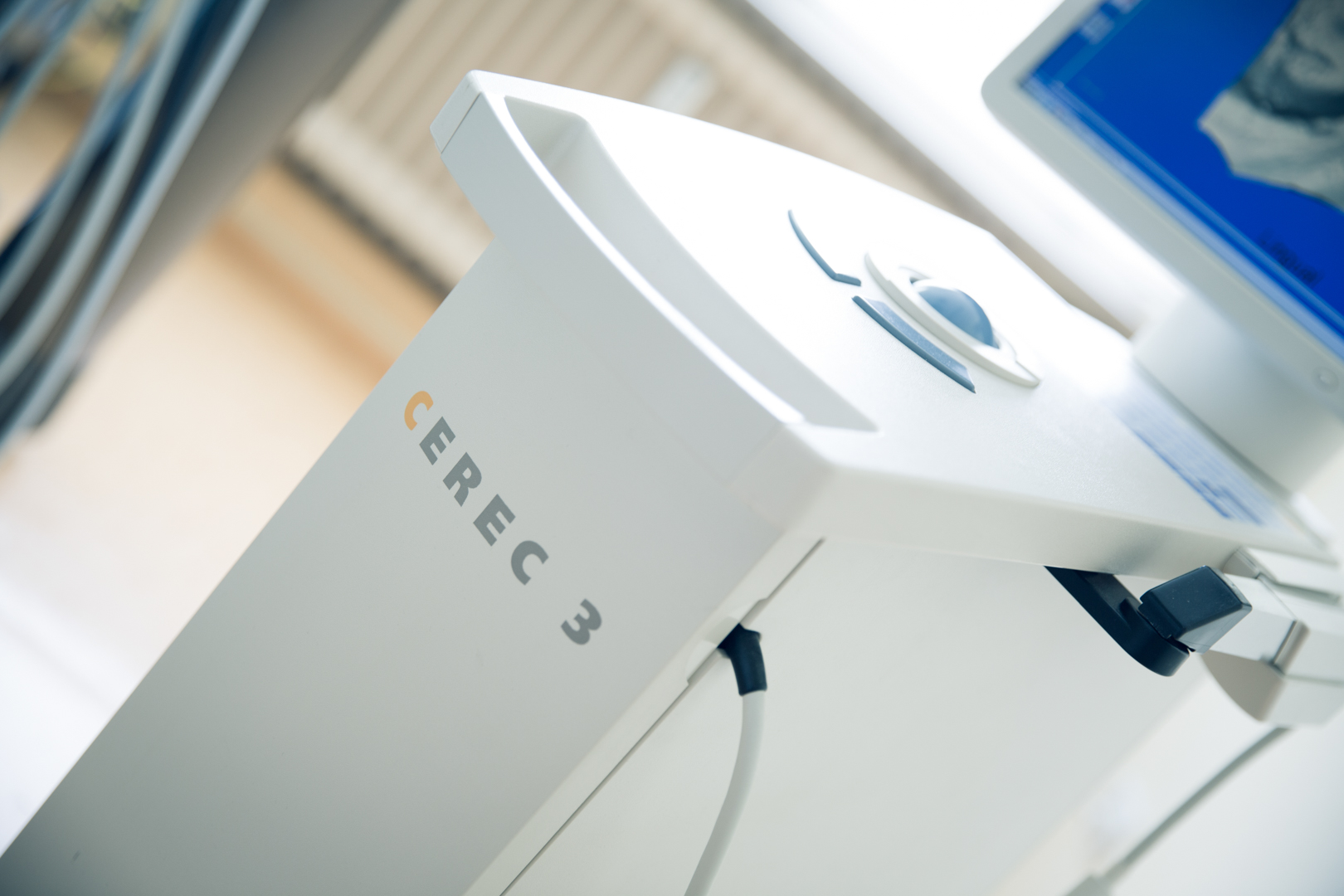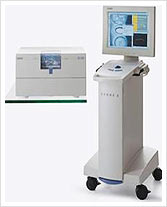  |
|---|
| The Cerec Apparatus Photos: approved by Sirona Dental Systems GmbH |
A tooth with deadened pulp tends to become fragile and can change color. In this case, a crown suffices. Crowns are also put on to living teeth if they are severely destroyed. The function of the crown lies in the restoration of the chewing mechanism and the correspondence with aesthetic requirements. Metal and ceramic crowns are designed to improve the aesthetic appearance of the mouth. Natural enamel transparency can be imitated as ceramic crowns are free of metal.
A hastened crown integration allows the so-called CEREC procedure.
The prepped tooth or model is photographed with a special camera.
Based on the data gathered a computer constructs the crown and mills it from a ceramic block.
For bleached teeth ceramic masses as well as Cerec-ceramic blocks are available in special colors.
Pin structure or synthetic insert
When the crown of a tooth has been completely destroyed, it is not necessary to extract the remaining root. In this case a synthetic root insert, the so-called pin, is manufactured. The precise imitation of the tooth’s canal form through the synthetic root insert allows the chewing pressure to be distributed between the root and the restored tooth stump, the latter of which later receives a crown.
Bridges (bridge dentures)
A bridge can be made from certain metal ceramics based on different alloys (inert metal alloys as well as medically bio-compatible special alloys). By precise, quality-appropriate pouring of metal it is possible to form the scaffold of a bridges-like prosthesis firmly, „easily“ and „delicately“.The anatomical form of the natural teeth is completely imitated. This is a vital precondition for the prevention of periodontal illnesses (infections, bleeding, discolorations, aching gums, formation of pathological pockets).
Meanwhile full-ceramic bridges, which are sharpened in a so-called CAD/CAM-procedure from a ceramic sleeve are available.
Removable dentures
Removable dentures are very popular because they can be produced simply and fast and have very few disadvantages. If they are to be worn only transitionally, they consist of plastic with hand-bent clips. If, however, the dentures are to be worn constantly, they consist of a combination of a special metal alloy (founding dentures) as a base and are made of a combination of a special metal alloy (model downpour prosthesis) as a base, with synthetic material and snythetic/ceramic teeth.
High quality molded dentures (hanger dentures)
The application of a metal hanger allows the chewing load to spread evenly between the mucous membrane and the remaining teeth. The dentures can be formed smaller, longer-lasting and more user-friendly. Thereby decreasing the time needed to get accustomed to the dentures. The hold of a molded denture can be created in a variety of ways. Telescope crowns, bolts, anchors, clips, hinges and many more are available.
Telescope crowns
With the connection to telescope crowns the irregular lever-like dental pressure and the resulting loosening of the supporting teeth is avoided. A telescope crown consists of two crowns. The first crown looks like a metal cap which is put on to the preserved tooth. The second crown is a part of the loose denture which has the form of the inside of the first crown and the outside of the natural tooth.
Complete prosthesis (removable denture)
A complete prosthesis is entirely made of synthetic material and plastic/ceramic teeth. The quality of a loose denture depends on the quality of the applied dental materials.
Prophylaxis Periodontology:
Individual prophylaxis
The path to a nice and healthy set of teeth an entire life long requires systematic care and attention.
Prophylaxis is the most important branch of dentistry. Disregarding these, merits all other measures as senseless. The biotope of the oral cavity influences one’s general well-being far more than is acknowledged or accepted. The mouth acts as the absorber of nutrients and enables us speech, feelings are expressed through it. In addition to being a prop to the lips and cheeks, the teeth are of great importance to the appearance of the face. Healthy teeth are a gift, underlining the feeling of general health.
Teeth and gums fallen ill are not hard to come by. A large percentage of the population is affected by oral diseases. Nevertheless, dentists can help to prevent the slow and often painful damage of teeth and the surrounding tissue. There are few aspects of dentistry that are as effective and indisputable as the measures of prevention. Following long-standing experience with prophylaxis and founded on the results of international research, dentists can offer a program of prevention which is successful when consequently followed through. Thus treatments for existing damages in tooth and gums are only sensible if an intensive, organized and controlled prophylaxis is pursued.
Possible steps of a prophylaxis treatment
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
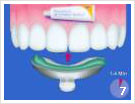 |
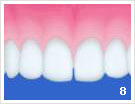 |
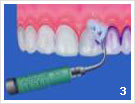
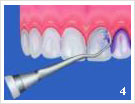
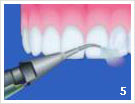
- Initial condition before the consultation
- Coloring of the layers
- Prof. cleaning with ultrasound
- Prof. cleaning with hand instrument
- Polishing of the teeth with powder ray device
- Polishing of the teeth with polishing paste
- Coating of the teeth
- Purpose of treatment: clean and healthy teeth
 |
 |
|---|
What distinguishes the systematic and organized individual prophylaxis from the standard prophylaxis?
No age limit
Also before the 6th and after the 18th year of age, many patients suffer from caries.
Dentists recommend the systematic individual prophylaxis for all age groups.
Measures
Dentists are aware that domestic dental care is not sufficient. That is why they apply professional mechanical teeth-cleaning during the systematic individual prophylaxis. Only using this method of prophylaxis treatment is the dentist able to use Fluoride in very small quantities sensibly and efficiently. Scientific knowledge determines the style and character of these measures.
Frequency
Frequency and expenditure of time for prophylaxis measures depend on the individual needs of the patient and are not limited by the regulations of the health insurance scheme.
Time Allocation
The available treatment time is determined individually. Good prophylaxis requires time and patience!
Parodontitus Treatment
Parodontitus Treatment – Prevention and care:
Parodontitus („vernacular“- Periodontosis) is the disease of the parodontium. Approximately 80% of all people suffer from this illness. Parodontitis is usually painless and stretches over many years. It is the result of inattentive oral hygiene. However, a partial diet that is poor in vitamins as well as the pleasure of excessive nicotine can also contribute to the development of the disease.
An initiating Parodontitis can be recognizable by symptoms such as bleeding gums and an uncomfortable aftertaste. By regular cleaning of the teeth and gum treatment, a variety of healthy foods as well as a semi-annual visit to the dentist Parodontitis can be avoided.
Etiopathology
With Parodontitis, the first occurance is always an inflammation of the gums surrounding the neck of the tooth. Then the disease progresses and penetrates into the depth of the parodontium, in which the teeth are embedded (alveolus). As the „bone cubicles“ become smaller and smaller, the retreating of the gums is unpreventable. The teeth become loose and interfere with speech and chewing. In most cases a removal of the teeth is unavoidable at this point.
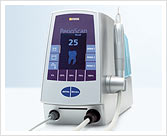 |
|---|
| Ultrasonic system PerioScan Photos: approved by Sirona Dental Systems GmbH |
Parodontitis development – early diagnosis
A Parodontitis can be recognized by the following features: the teeth appear longer because the gums withdraw, bad breath occurs, the front teeth protrude and jot outwards, tooth gaps appear where there were none before. Early recognizable symptoms are an increase in the bleeding of the gums and a disagreeable „aftertaste“.
Parodontitis development – self-aide
A Parodontitis can be avoided by regular cleaning of the teeth and gum treatment. A well balanced, healthy diet likewise plays a big role, as well as the semi-annual visit to the dentist. If the gums have a pale-pink color, they are healthy. Fine, pointy leakages, called papillae, fill the spaces between the teeth.
Inflamed gums acquire a strong red color and are inclined to bleeding. Brushing the teeth may be very painful.
Precautionary brushing – but properly!
Below, a widely used method for brushing teeth is introduced.
According to the respective age (child or adult), taking possible illnesses into consideration, according to whether the teeth are cleaned manually or electrically, there are individual differences in the optimal cleaning technique. We would be pleased to introduce you to the technique which best suites you in a visit to our practice.
After every meal (3 x daily) the teeth should be cleaned. This way no damaging dental plaque can form.
The recommended cleaning time is 3 minutes.
The mouth should be rinsed first. The water is pressed through the spaces between the teeth, ridding the mouth of fresh leftovers.
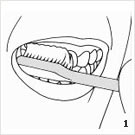
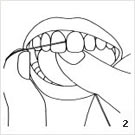
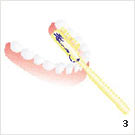
Following this, the exterior surfaces of the teeth should be cleaned first with toothpaste and a toothbrush. With a slightly open mouth one should begin with the last molar in the left upper jaw. Applying light pressure, small rotary movements on 2 – 3 teeth at a time should be performed for approx. 10 times. Next the toothbrush is placed a little further to the front. Continuing in this manner, the teeth should be brushed in small segments, until the right side of the upper jaw is cleaned. The same procedure should be performed in the lower jaw. The inner surfaces should not be forgotten. Finally all chewing surfaces should be cleaned. Brushing forward and backward is now permitted. The mouth should be rinsed again thoroughly, so that all loosened leftovers are removed. However, one should not exercise too strong pressure when cleaning the sides of the teeth. The delicate tissue surrounding the teeth withdraws as the dental neck is “scrubbed” free. The maximum pressure should correspond to about 200g. It is the time that is vital, not the strength.
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|
- Cleaning with toothbrush
- Cleaning with dental floss
- Motion sequence inside
- Motion sequence outside
Still, there are many other aspects which should be taken into consideration. We, as a practice team, can provide you with many more tips concerning a prophylaxis.
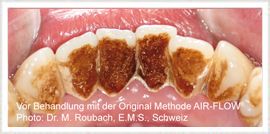
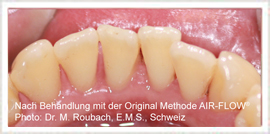
What is to be done when the first signs of Parodontitis appear?
The first path leads to the dentist’s office. Here the extent of Parodontitis and the preceding steps can be determined.
Usually a professional cleansing of the teeth follows. Then, after various pretreatment appointments, the area is cleaned deeply in the pocket. As a general rule special hand instruments are applied during this procedure. Optimizing the result of the treatment, the ultrasound scanners, which conduct especially fine movements, are used in our practice.
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|
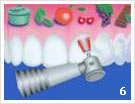
- The Vector™
- Pictures 2 – 4: The Vector™ in use
In addition to Soniflex, which performs elliptical movements, the vector system is used. A powder-liquid mixture is moved into ultrasonic oscillations. Now it is possible to rid the tooth of deposits and polish it.
As an additional supporting measure the laser can be used. It is able to rid the gum pockets of bacteria without requiring any anesthetic drugs. Furthermore it can remove infected tissue, which enables the gums to grow around the teeth once more (deepithelialization).
Laser dentistry:
Laser
Every laser has it’s own special field of operation. Our practice for innovative dentistry offers various possibilities of treatment to the patient, as we have several laser systems at our disposal.
The practice uses „LaserSmile™“, „ezLase™“, „WaterlaseMD™“ and the „Diagnodent™“ laser.
Advantages of laser applications
Lasers can be applied in nearly all dental areas of treatment.
Simplicity and quickness, the absence of post surgical bleeding and edemas are characteristic of laser treatment. Additional preventions are not necessary. As a rule there are no restrictions concerning the patient’s dietary and general living habits.
- Gentle and effective
- Little or no numbing
- Little or no bleeding
- The healing process is accelerated
- Less pain
- Vibrations causing pain and the heat associated with drilling are non-existent in laser use.
During the application of a laser, an interaction occurs between the special wavelength and the molecule structure of the tissue being worked on. According to the setting of the laser, a thermal effect more or less appears during the application. The special thing about this intervention is that it is often treatable without numbing, in other words there is little or no bleeding and the healing process is accelerated.
Operational field of different laser types
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
Laser in surgery
Another advantage in the application of laser technology in dental surgery is the fact that during an operation the patient can remain completely free of stress because they don’t see the customary scalpel. Blood vessels are hermetically closed with laser radiation, allowing a virtually blood-free incision. Thus patients who are inclined to bleeding can be helped with laser treatment.
Laser beams kill the pathological micro flora (bacteria and viruses) in the area of the surgical intervention, reducing the likelihood of a post surgical complication.
Application fields of the WaterlaseMD ™
General
- Desensitization
Filling therapy
- Anesthetize
- Work on enamel
- Work on dentin
- Corrosion of surfaces
- Removal of caries
- Conditioning and disinfection of cavities
Periodontics
- Disinfection of the root canal
- Treatment of the fistula canal
Prosthetic
- Opening of the sulcus before the molding
- Lengthening of the clinical crown
Periodontics
- Removal of infected tissue
- Deepilisation of the gum pockets
- Disinfection of the gum pockets
Surgery
- Opening of abscesses
- Removal of gum pieces
- Removal of lip and tongue strings
- Removal of tissue
- Herpes treatment
- Aphtha treatment
- Bone treatment
- visible enlargement of the jaw comb
- Root tip resection
- Coagulation
Implantation
- Location of the implant position
- Tissue cut
- Implant opening
- Opening of the maxillary sinus considering the area of the nasal sinuses membrane
- Therapy concerning implantation in general
Laser for child dentistry
 The first teeth automatically call for the first meeting with the dentist. However, this first acquaintance should not happen when chocolate and co. leave their first tracks on the teeth. The opportunity to win the trust of a child appears a lot earlier, when their parent visits the practice for a control for example.
The first teeth automatically call for the first meeting with the dentist. However, this first acquaintance should not happen when chocolate and co. leave their first tracks on the teeth. The opportunity to win the trust of a child appears a lot earlier, when their parent visits the practice for a control for example.
Children need very special attention. Not only in their development and everyday life, but also during dentist’s visits. Unknown surroundings, uncertainty about what will happen and whether or not they will have to experience pain causes fear. They feel more readily afraid than adults, acknowledge gestures, moods and behavior more clearly than speech and feel unprotected and helpless more quickly.
During the consultation with children about the visit to the dentist, terms like „drill“, „soon it will be a syringe“, „keep still“, „cutting“, „it will soon be over“, etc. should absolutely be avoided.
 With regular dental care and oral hygiene, as well as healthily balanced food from an early age on, teeth stay healthy and strong for a long time. The first visits to the dentist can correspond to „test-sitting on the mobile patients chair“. If a treatment is eventually necessary, the practice and surroundings are already familiar and there is no reason to develop a feeling of fear.
With regular dental care and oral hygiene, as well as healthily balanced food from an early age on, teeth stay healthy and strong for a long time. The first visits to the dentist can correspond to „test-sitting on the mobile patients chair“. If a treatment is eventually necessary, the practice and surroundings are already familiar and there is no reason to develop a feeling of fear.
Further positive experiences and treatments without traumas not only require tooth prophylaxis and contact appropriate for children, but also contemporary and innovative technology.
During the application of the WaterlaseMD ™ water is evaporated by means of laser energy. In this way generated kinetic energy can be used as a dentist’s drill, without actually drilling. The treatment is virtually painless and therefore an anesthetic remains unnecessary in most cases, a syringe and the uncomfortable numb feeling are avoided.
The usually annoying and fear-inducing vibration of a drill is completely absent and bleeding seldom occurs because the treated place is bounded by the laser beam hermetically. Thanks to high precision work, the injured areas are treated by the laser beam point-precisely, preserving healthy tissue and enabling better protection.
Alone in child dentistry, the laser shows very positive application.
Laser
Every laser has it’s own special field of operation. Our practice for innovative dentistry offers various possibilities of treatment to the patient, as we have several laser systems at our disposal.
The practice uses „LaserSmile™“, „ezLase™“, „WaterlaseMD™“ and the „Diagnodent™“ laser.
Advantages of laser applications
Lasers can be applied in nearly all dental areas of treatment.
Simplicity and quickness, the absence of post surgical bleeding and edemas are characteristic of laser treatment. Additional preventions are not necessary. As a rule there are no restrictions concerning the patient’s dietary and general living habits.
- Gentle and effective
- Little or no numbing
- Little or no bleeding
- The healing process is accelerated
- Less pain
- Vibrations causing pain and the heat associated with drilling are non-existent in laser use.
During the application of a laser, an interaction occurs between the special wavelength and the molecule structure of the tissue being worked on. According to the setting of the laser, a thermal effect more or less appears during the application. The special thing about this intervention is that it is often treatable without numbing, in other words there is little or no bleeding and the healing process is accelerated.
Operational field of different laser types

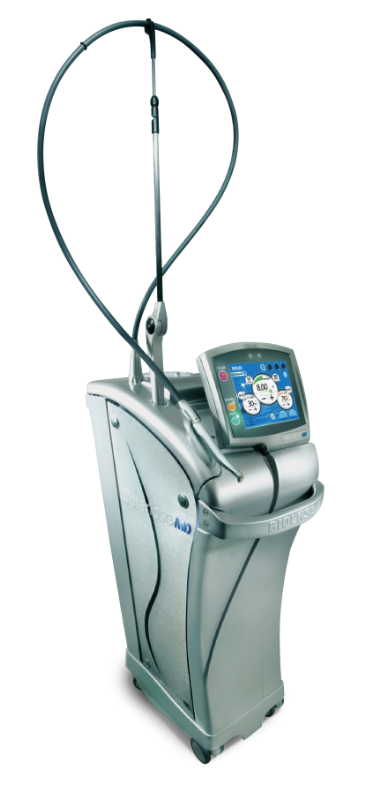
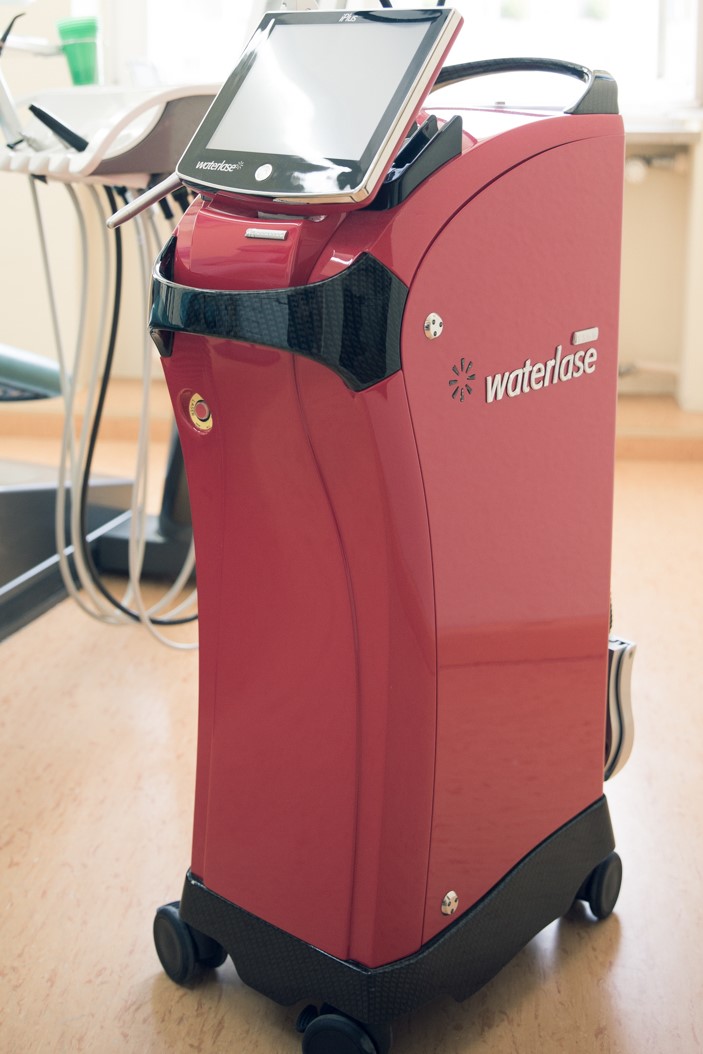
- The WaterlaseMD ™ is the worldwide leading laser for practically painless dental treatment. The Hydro kinetic Er.Cr.:YSSG laser enables the surgeon a clean and exact cut. Also, the hard tissue has a high wastage rate which produces better results than the customary Er:Yag lasers – namely in a very diverse indication spectrum. In addition, many problems with drilling, for example, the micro fractures which weaken the stability of the tooth, are avoided. Moreover, in addition to virtually no pain a better hold of the fillings through an optimized surface structure of the tooth and a caries protective result are effected. With the use of the WaterlaseMD ™ we, as a dentist’s practice, treat the patient with careful and precise technology!

- The iPlus is the FOLLOW-UP LASER on the MD with even shorter pulses and thus increased preparation speed with less sensitivity for the patient. The menu navigation is more intuitive and the setting is understandable even for patients.

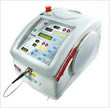
- The LaserSmile™ is essentially used for the bleaching of teeth, as well as within the confines of the root canal and gum treatment.

- The epicX diode laser is a further development of the ezLase with intuitive operation and higher performance values. The epicX is mainly used in the context of surgical interventions, root canal and gum treatments.

- The EzLase ™ is mainly used within the scope of surgical interventions, root canal and gum treatments.

- The iLase diode laser is a small, practical diode laser. The iLase is mainly used in the context of root canal and gum treatments. But it can also be used in other areas.

- The Diagnodent laser ™ is exclusively applied in the absolutely painless cavity detection. It also impresses by the fact that it recognizes carious defects not visible to the human eye.

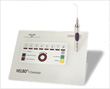
- With dye and laser light, the HELBO therapy is painless and quick to use. & nbsp; It is a purely local therapy to destroy the bacteria and fungi that cause inflammation and, above all, has no negative side effects .
Laser in surgery
Another advantage in the application of laser technology in dental surgery is the fact that during an operation the patient can remain completely free of stress because they don’t see the customary scalpel. Blood vessels are hermetically closed with laser radiation, allowing a virtually blood-free incision. Thus patients who are inclined to bleeding can be helped with laser treatment.
Laser beams kill the pathological micro flora (bacteria and viruses) in the area of the surgical intervention, reducing the likelihood of a post surgical complication.
Application fields of the WaterlaseMD ™
General
- Desensitization
Filling therapy
- Anesthetize
- Work on enamel
- Work on dentin
- Corrosion of surfaces
- Removal of caries
- Conditioning and disinfection of cavities
Periodontics
- Disinfection of the root canal
- Treatment of the fistula canal
Prosthetic
- Opening of the sulcus before the molding
- Lengthening of the clinical crown
Periodontics
- Removal of infected tissue
- Deepilisation of the gum pockets
- Disinfection of the gum pockets
Surgery
- Opening of abscesses
- Removal of gum pieces
- Removal of lip and tongue strings
- Removal of tissue
- Herpes treatment
- Aphtha treatment
- Bone treatment
- visible enlargement of the jaw comb
- Root tip resection
- Coagulation
Implantation
- Location of the implant position
- Tissue cut
- Implant opening
- Opening of the maxillary sinus considering the area of the nasal sinuses membrane
- Therapy concerning implantation in general
Laser for child dentistry
 The first teeth automatically call for the first meeting with the dentist. However, this first acquaintance should not happen when chocolate and co. leave their first tracks on the teeth. The opportunity to win the trust of a child appears a lot earlier, when their parent visits the practice for a control for example.
The first teeth automatically call for the first meeting with the dentist. However, this first acquaintance should not happen when chocolate and co. leave their first tracks on the teeth. The opportunity to win the trust of a child appears a lot earlier, when their parent visits the practice for a control for example.
Children need very special attention. Not only in their development and everyday life, but also during dentist’s visits. Unknown surroundings, uncertainty about what will happen and whether or not they will have to experience pain causes fear. They feel more readily afraid than adults, acknowledge gestures, moods and behavior more clearly than speech and feel unprotected and helpless more quickly.
During the consultation with children about the visit to the dentist, terms like „drill“, „soon it will be a syringe“, „keep still“, „cutting“, „it will soon be over“, etc. should absolutely be avoided.
 With regular dental care and oral hygiene, as well as healthily balanced food from an early age on, teeth stay healthy and strong for a long time. The first visits to the dentist can correspond to „test-sitting on the mobile patients chair“. If a treatment is eventually necessary, the practice and surroundings are already familiar and there is no reason to develop a feeling of fear.
With regular dental care and oral hygiene, as well as healthily balanced food from an early age on, teeth stay healthy and strong for a long time. The first visits to the dentist can correspond to „test-sitting on the mobile patients chair“. If a treatment is eventually necessary, the practice and surroundings are already familiar and there is no reason to develop a feeling of fear.
Further positive experiences and treatments without traumas not only require tooth prophylaxis and contact appropriate for children, but also contemporary and innovative technology.
During the application of the WaterlaseMD ™ water is evaporated by means of laser energy. In this way generated kinetic energy can be used as a dentist’s drill, without actually drilling. The treatment is virtually painless and therefore an anesthetic remains unnecessary in most cases, a syringe and the uncomfortable numb feeling are avoided.
The usually annoying and fear-inducing vibration of a drill is completely absent and bleeding seldom occurs because the treated place is bounded by the laser beam hermetically. Thanks to high precision work, the injured areas are treated by the laser beam point-precisely, preserving healthy tissue and enabling better protection.
Alone in child dentistry, the laser shows very positive application.
Anxiety patients:
Anxiety patients
Dear patients
In Germany, according to surveys, 70% of the population feel uncomfortable before a visit to the dentist, 20% of them are extremely anxious and 5% avoid visiting the dentist completely.
These 5% suffer from the so-called dental phobia, which affects millions of people. < / p> The fears have very diverse origins, whereby “the uncertainty about what will happen at the dentist” and the trauma experienced during childhood are mentioned most frequently when visiting the dentist.
The fears that develop from this affect all possibly painful, invasive & nbsp; Interventions, especially the drill, a root canal treatment, the “pulling” of a tooth, but also the syringe to eliminate pain.
These patients & nbsp; experience their fears during a visit to the dentist not only psychologically but also physically: & nbsp;
The symptoms range from dizziness, nausea and sweating to palpitations and circulatory collapse.
How does an anxiety patient differ from a phobia patient?
Here is a small example to illustrate the difference:
A man drives to the airport, checks in, sits on the plane and takes off. After a while he sees smoke on the engine, then flames and hears the captain’s announcement that there will be a landing due to technical problems. The man has sweats, palpitations, wet hands, so fear, and justified fear.
Another man drives to the airport, checks in and takes off. During the flight, he imagines the engine full of smoke and flames and gets wet hands, sweats and a racing heart. This man is scared. & nbsp;
Another man who is sitting in the taxi to the airport and now imagines the situation in the plane with the engine burning. He also gets wet hands, sweats and a racing heart, whereupon he drives back home and skips the planned trip. This man has a phobia.
Consequences
Those affected mostly avoid any ZA visit and live / suffer with the consequences:
- Carious, discolored teeth with partly large defects
- Gum disease and bad breath
- Pain, resulting in increased use of painkillers
- Shame, and much more
- Often the result is a severe reduction in the quality of life and the social isolation of those affected.
General anesthesia
These patients often want treatment under general anesthesia.
This decision is particularly problematic for patients who cannot be completely rehabilitated in one session under general anesthesia or who have chronic diseases Suffer. The risks and side effects should also not be ignored.
But what about general anesthesia & nbsp; There is no way to cure someone of their phobia!
This is not intended to condemn general anesthesia, but should only be chosen carefully and with the strictest indication.
The phobia of dental treatment is a recognized mental illness and in pronounced cases can also be treated as such by a psychotherapist.
Sometimes, through close cooperation between the dentist and psychotherapist, an improvement in the condition (ability to treat) and healing can be achieved.
So how can patient and dentist? become a team despite all the difficulties?
- Talk to us openly about your problem so that your dentist and practice team can adapt to your situation. There are many patients who are extremely anxious and do not need to be ashamed!
- Let yourself be fully informed before the treatment and discuss with your dentist which treatment steps you already feel ready for.
- We take time for you! Our team is experienced in dealing with phobia patients and will guide you through the treatment in a friendly manner.
- You may need to bring someone with you who has your trust and supports you.
- Clarify the need for treatment and set goals.
- We offer you painless to painless treatments with the help of the laser, which works without contact and without the familiar drilling noise.
- If you are in severe pain, contact a dentist you trust as quickly as possible. In any case, you can also be helped with gentle methods (including the laser).
- With a previously determined treatment plan, you know what to expect and have the opportunity to adapt to it.
An example for the 1st appointment with us:
After you have answered our anamnesis sheet with a few questions, you will be taken to one of our treatment rooms, where you will first sit down and & nbsp; get to know your dentist. I.e. You report on the reason for your visit, your expectations and wishes. The doctor will then advise you on various treatment options. educate, e.g. explain the use of the laser.
This is followed by an examination of the oral cavity, with mirrors and blunt instruments (possibly the Diagnodent, a non-contact diagnostic laser) and X-rays may be taken. & nbsp;
Very important: & nbsp; You should never feel at the mercy! You have the option of interrupting the treatment at any time and influencing the further course.
Finally, your dentist will explain the necessary treatments to you and answer your questions. You can then plan further appointments and their schedule together.
Useful information:
Dental medicine concerning flying and diving
Everyone who dives and many who have already flown have noticed that the pressure in the ears changes considerably. However, this is only noted if the surroundings change.
The altered pressure is also found in other body organs. The teeth and the gums, the jaw joint and the facial muscles, thus the whole oral-, jaw-, and facial area, are also affected.
Reasons other than pressure- and temperature change, are vibrations and stress. This means that dental medicine concerning diving and flying inevitably has to consider environmental factors in certain surrounding relations (in particular: pressure fluctuations).
The influence on the dental-, oral-, and jaw systems is especially likely to occur when there have been previous illnesses or therapies which have not taken surrounding environmental factors into account. Therefore dental diagnostics must take different environmental factors into consideration.
Irritated wisdom teeth and infected teeth along the root canal are especially affected. The phase in which the surrounding relations change is the point in which most problems appear.
Concerning aviation, the discomfort appears primarily during take off and in the landing phase. Since during diving a change in the environmental surroundings happens much faster, many problems are to be expected here too.
Names for such illnesses are usually: Barodontalgie, Dysbarismus, Aerodontalgie, Aerodontopathie, and pressure disturbance.
 |
 |
|---|---|
| a pilot license since 1995 | Safety diver since 1998 (Professional Association of Diving Instructors) |
The world of dentistry
For more detailed information on all topics and of course for the individual handling of your personal concerns, we would be happy to advise you personally!
We have also put together a little dentistry here:
An adult has 28 teeth (+ possibly 4 wisdom teeth).
The set of teeth consists of 8 incisors, 4 canines and 16 molars.
In order to understand how toothache develops and why you experience it that way, let us introduce the tooth at this point:
It has a hard shell and an extremely sensitive core in which its nerves and blood vessels are embedded.
This soft bed is the pulp, the pulp. Except for a small opening to the jawbone through which the vessels run, it is surrounded by the dentin, the dentin.
Dentin is hard but elastic and can be reproduced for life. In contrast to the outer armor, the tooth enamel.
The root cement encompasses the tooth from the neck of the tooth to the tip of the root. The tooth is embedded in the tooth socket or alveolus. It is framed by the jawbone, which in turn is surrounded by the gingiva, our gums.
The tooth is prone to damage or disease. A distinction must be made between diseases of the tooth itself and those of the holding apparatus.
The most common damage to the tooth is caused by bacteria and is commonly known as tooth decay. The bacteria destroy the tooth enamel, eat their way through the dentin and pulp.
The tooth alerts the entire system via the nerves in the form of pain, but since all tooth nerves are bundled in one large jaw nerve, the exact focus of pain can often only be determined by the dentist.
The preferred focus of disease in the tooth supporting system is the gums. As part of the oral mucosa, it is very susceptible to bacteria and, as a result, also to inflammation.
In many cases, bleeding gums (a symptom of the mostly harmless gingivitis) and mild „periodontitis“ can be eliminated by thoroughly removing the microbial plaque during dental care at home.
In the case of severe periodontal disease, the substance of the teeth holding apparatus is attacked: the gums recede, the teeth become longer and longer.
But it doesn’t have to come to that.
Öffnungszeiten
MO 10.00 - 19.30 Uhr
DI 07.30 - 14.30 Uhr
MI 10.00 - 18.30 Uhr
DO 07.30 - 14.30 Uhr
FR gerade Woche
10.00 - 18.00 Uhr
FR ungerade Woche
7.30 - 14.30 Uhr
